Class 6 Geography Chapter 2 – Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Notes
On this page find class 6 geography chapter 2 notes. This chapter is about Globe Latitudes and Longitudes. We will also provide PDF download at the end of the notes for students so they can revise their chapter for their tests and exams.
Overview of class 6 geography chapter 2
Understanding the Earth’s geography requires grasping concepts like latitudes and longitudes, which are imaginary lines that help locate places on the planet. Longitudes run from the North Pole to the South Pole. Latitudes go along the equator. These lines contribute to the classification of Earth into different heat zones, such as the Torrid, Temperate, and Frigid Zones, which result from varying angles of the sun’s rays.
Additionally, longitudes are essential for determining time zones and maintaining a consistent time system worldwide. Countries adopt standard times based on a central meridian, like India’s use of the longitude of 82°30’E for Indian Standard Time (IST). This system enables better coordination and communication among countries, while the International Date Line ensures a uniform calendar system across the globe. By learning these fundamental geographical concepts, students can better appreciate the interconnected nature of the world and the factors that influence our daily lives.
Globe latitudes and longitudes class 6 notes
Earth’s Shape and Globe Representation
- Earth is not a perfect sphere; it is slightly flattened at the North and South Poles and has a bulge in the middle.
- Globes are true models of Earth in miniature form and come in various sizes and types.
- Globes can be rotated to mimic Earth’s rotation, and they accurately represent countries, continents, and oceans.

Latitudes and Earth’s Division
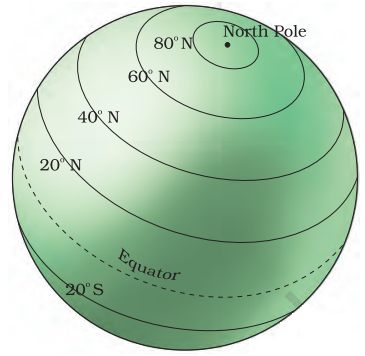
Latitudes:
Imaginary lines running parallel to the Equator are used to locate places on Earth.
Equator:
An imaginary line at 0° latitude divides Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
North and South Poles:
Two points at 90° N and 90° S latitudes, where Earth’s axis passes through.
Parallels of latitudes:
All parallel circles from the Equator up to the poles.
Important Parallels of Latitudes
These latitudes help define Earth’s heat zones.
Tropic of Cancer (23½° N):
Located in the Northern Hemisphere.
Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S):
Located in the Southern Hemisphere.
Arctic Circle (66½° N):
North of the Equator.
Antarctic Circle (66½° S):
South of the Equator.
Heat Zones of the Earth
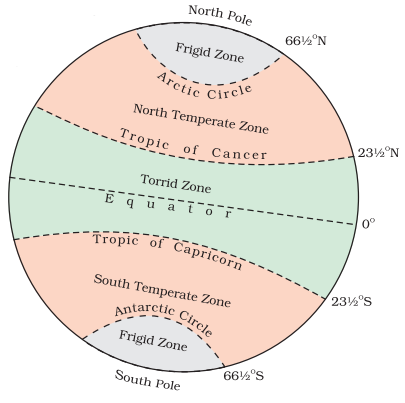
Torrid Zone:
Area between Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, receiving maximum heat due to the overhead sun.
Temperate Zones:
Areas between Tropic of Cancer and Arctic Circle (Northern Hemisphere) and Tropic of Capricorn and Antarctic Circle (Southern Hemisphere) with moderate temperatures due to the sun’s rays hitting at a lower angle.
Frigid Zones:
Areas between Arctic Circle and North Pole (Northern Hemisphere) and Antarctic Circle and South Pole (Southern Hemisphere), characterized by very cold temperatures because the sun’s rays are always slanting and provide less heat.
Longitudes and Precise Location
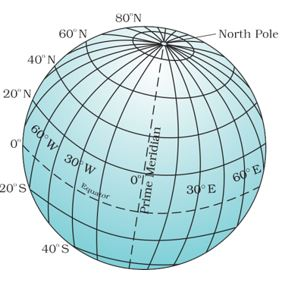
Longitudes:
Imaginary lines running from North Pole to South Pole, used in conjunction with latitudes to precisely locate places on Earth.
Prime Meridian:
0° longitude line passing through Greenwich, UK, dividing Earth into Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
Longitude Measurement:
Longitudes are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds, with 180° east and 180° west from the Prime Meridian.
Longitude and Time Calculation
Earth’s Rotation:
Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, which means 15° per hour or 1° in 4 minutes.
Time Differences:
Places east of Greenwich are ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), while those west are behind GMT.
Local Time:
Determined by the position of the sun, with all places on a given meridian having the same local time.
Standard Time and Time Zones
The necessity for Standard Time:
Uniform time is needed for efficient communication, transportation, and daily activities across various longitudes.
Indian Standard Time (IST):
Based on 82°30′ E longitude, IST is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of GMT.
Time Zones:
Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each covering 15° of longitude. Countries with large longitudinal extents, like Russia, may have multiple standard times.
Standard Time in Countries with Large Longitudinal Extent
Adoption of Multiple Standard Times:
Some countries with vast longitudinal extents, like Russia, adopt more than one standard time to accommodate regional differences.
Russia’s Standard Times:
Russia has eleven different standard times due to its vast size and longitudinal extent.
International Date Line (IDL)
Definition:
The International Date Line is an imaginary line located at 180° longitude (both East and West), opposite the Prime Meridian, where the date changes by one day.
Function:
The IDL helps maintain a uniform calendar system globally and separates one day from the next.
Latitude and Longitude Grid System
Grid System:
The grid system created by the intersection of latitudes and longitudes helps in locating any point on Earth easily.
Example:
Dhubri in Assam is situated at 26° N latitude and 90° E longitude. By finding the intersection of these lines, the location of Dhubri can be determined.
Questions and answers based on this chapter
- What are latitudes and longitudes, and how do they help in locating places on Earth?
- Name four important parallels of latitudes and their corresponding degrees.
- How are the Earth’s heat zones (Torrid, Temperate, and Frigid Zones) determined by the angle of the sun’s rays?
- Why is it necessary for countries to adopt a standard time based on a central meridian, and how does this system help in communication and coordination among countries?
- What is the International Date Line, and how does it contribute to maintaining a uniform calendar system across the globe?
class 6 geography chapter 2 notes pdf
Download these globe latitudes and longitudes class 6 notes pdf for free.
Leave a Reply