What is the full form of LED?
LED Full Form: Light Emitting Diode. LED is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. Developed in the early 1960s, LEDs are now widely used in various applications. They are known for their energy efficiency and long life. Unlike traditional bulbs, LEDs do not have a filament. They light up instantly and can emit a range of colours.
LEDs are used in displays, lamps, and even in medical devices. Their small size and durability make them ideal for many uses. This technology represents a significant advancement in lighting and electronic displays.
Now that we know the LED Full Form, let us look at the physics behind LEDs, how they work, the different types of LEDs, and their applications.
Understanding LEDs
LED Working Principle
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current is passed through it. The light emission happens due to a phenomenon called electroluminescence.
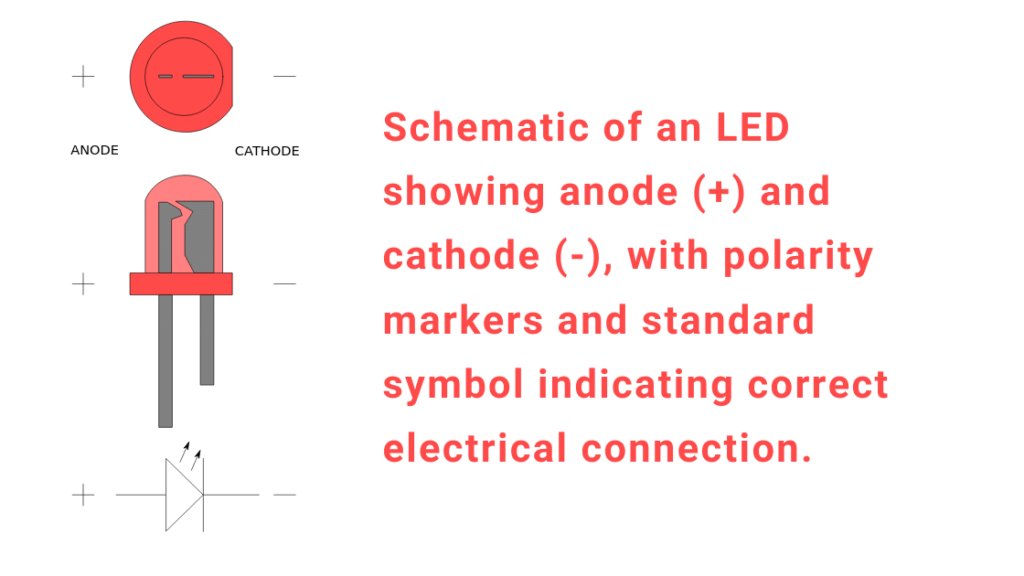
The basic structure of an LED consists of two regions of semiconductor material – a p-type with excess holes (positive charge carriers) and an n-type with excess electrons (negative charge carriers). These two regions are formed by doping the semiconductor material, usually gallium arsenide (GaAs) or gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP).
The p-type and n-type regions are connected together in a junction. When a voltage is applied across this p-n junction, the electrons from the n-region get pushed towards the p-region and the holes from the p-region get pushed towards the n-region.
As the electrons move across the junction, they fill holes present in the p-type region. Similarly holes move across to the n-type region and fill electron states there. When an electron fills up a hole or a hole occupies an electron state, energy is released in the form of a photon or light quantum.
The wavelength or colour of light emitted depends on the semiconductor material used and the doping levels. By changing the material and doping, LEDs can be made to emit different coloured lights – red, green, blue, etc.
The basic LED working principle involves movement of electrons and holes across a semiconductor p-n junction, transitions between their energy states and release of light photons due to these transitions. External voltage supply provides the means for this movement of charge carriers.
Types of LED
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, come in various types, each suited for different applications. Here are some common types:
For General Lighting
- High-Power LEDs: Used in industrial lighting, streetlights, and areas requiring high-intensity light. They are energy-efficient and have a long lifespan.
- COB LEDs (Chip On Board LEDs): Ideal for LED light bulbs and automotive headlights, offering high brightness and efficient light distribution.
For Displays and Screens
- Alphanumeric LEDs: Employed in digital displays like electronic billboards, public transport signs, and digital clocks, capable of showing numbers, letters, and symbols.
- RGB LEDs: Common in decorative lighting and display screens, these LEDs can produce a wide spectrum of colours by combining red, green, and blue light.
- SMD LEDs (Surface-Mount Device LEDs): Used in various electronic devices, these are integral to modern flat-screen TVs, smartphones, and digital signage.
For Indicators and Signalling
- Miniature LEDs: Found in mobile devices, calculators, and remote controls, perfect for small-scale, low-power indication.
- Flashing LEDs: Used in safety and alarm systems, these LEDs draw attention by blinking at a specific frequency.
- Bi-Colour and Tri-Colour LEDs: Often used in devices that require multiple indicator lights in a small space, such as battery charging indicators.
For Specialized Applications
- Application-Specific LEDs (AS-LEDs): Tailored for specific uses like automotive lighting, camera flashes, and traffic signals.
- Infrared LEDs (IR LEDs): Essential in remote controls, night-vision equipment, and optical sensors, these emit light in the infrared spectrum.
Applications of LEDs
Here are some of the major applications of LEDs:
- Display and Signage:
LED displays like LED walls, video walls and message displays are used for advertising, events, transportation information etc. Extremely high brightness allows visibility. - General and Decorative Lighting:
Used extensively for ambient lighting in homes, offices, shops, restaurants etc. Also used in landscape lighting and for lighting pathways, gardens etc. - Automotive Lighting:
LED headlamps, turn indicators, brake lights provide brightness, low power consumption and long life. Useful in dashboards and interiors as well. - Mobile Displays:
OLEDs and flexible LEDs are used in mobile phone screens, smart watch displays, etc. Provide crisp images with wide viewing angles. - Traffic Lights and Signals:
The long lifetimes and low maintenance make LED signals ideal for roads, railways and air traffic control. Help avoid accidents. - Medical Devices:
Instruments for diagnosis use LEDs for illumination and examination of body cavities. Used in phototherapy for treatment. - Horticulture:
LED grow lights enhance plant growth in enclosed spaces and greenhouses. Enable urban farming solutions.
Characteristics like high brightness, energy efficiency and compact size allow LEDs to serve lighting applications across transportation, infrastructure, horticulture, healthcare etc. providing safety and sustainability.
Science Related Full Forms
Leave a Reply